Did You Know?
WHAT IS VISCOSITY?
Viscosity is the thickness, or rate of fluidity, of engine oil. In general, high viscosity provides more protection of engine components but greater fluid resistance, resulting in slower engine start-ups, decreased performance, and increased fuel consumption.
VISCOSITY AND TEMPERATURE
Generally, the higher the temperature of the oil, the lower the viscosity. At the highest temperatures, decreased viscosity results in engine wear.

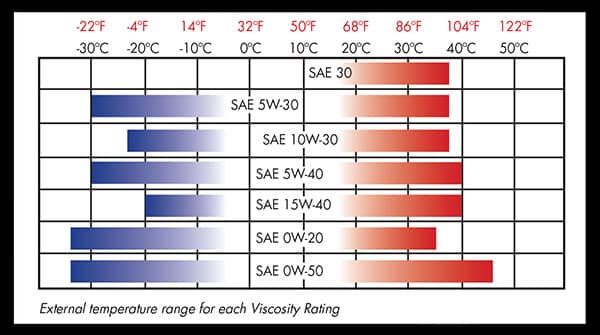
Single vs. Multi
Engine oil with a single grade viscosity (such as SAE 30) has a much smaller range of external temperature conditions.
Multi grade viscosity is important for ensuring engine protection in use outside of moderate external temperature ranges.
Most passenger vehicles are recommended to use multi grade, lower viscosity oil due to technological improvement providing increased fuel economy.
How to Read Viscosity Ratings
Example: SAE* 5W-30
5W = EXTERNAL RATING
“W” stands for “Winter,” or the rating for external temperatures.
A lower number indicates better fluidity at lower temperatures.
A “0W” oil has the least resistance at startup and cold temperatures.
30 = INTERNAL RATING
This number indicates oil’s viscosity at high internal temperatures, when the engine is running.
Higher numbers indicate “thicker” oils at 100ºC / 212ºF.